Mold growth inside your car can be a persistent problem, especially in humid climates or after water damage. Not only is mold unsightly, but it can also pose health risks to you and your passengers. Fortunately, eliminating mold from your vehicle doesn’t have to be a daunting task. This guide outlines 11 essential steps to safely rid your car of mold while protecting both your health and your vehicle’s interior.
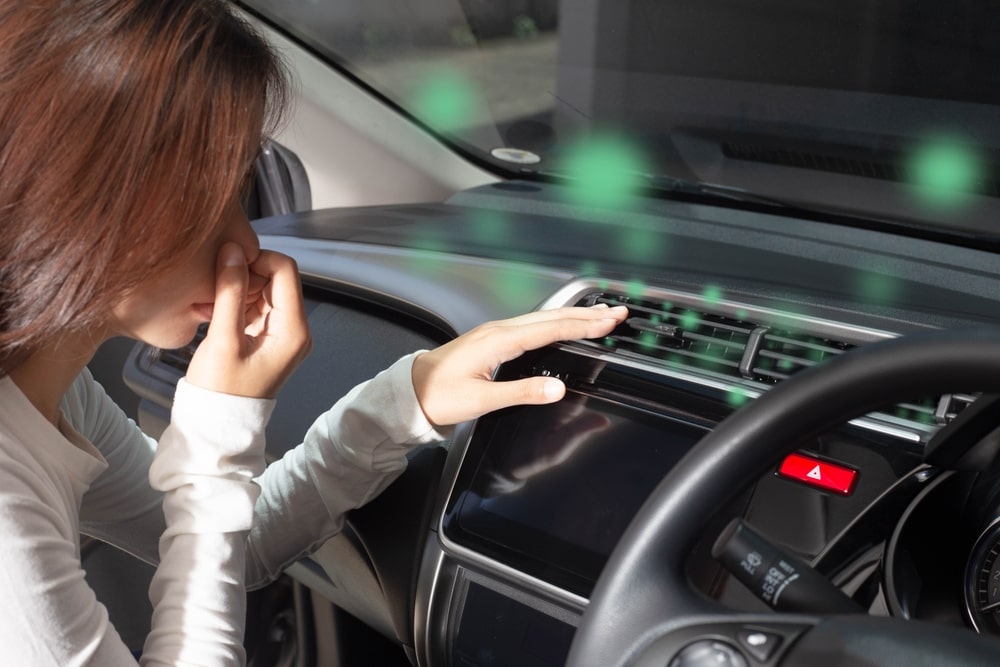
Nothing sours a morning commute like flipping on your car’s AC and being greeted by a musty, mildewy blast instead of fresh air. If you’ve noticed a persistent damp smell or seen unsightly spots creeping across your car’s interior, you’re facing a common yet serious problem: mold in cars. This fungal foe not only damages your vehicle’s aesthetics but poses real health risks, particularly for those with allergies or respiratory issues.
Every day, countless drivers unknowingly transport this hidden hazard, turning what should be a safe space into a health risk on wheels. If you’re among them, it’s crucial not just to remove the mold, but to understand why it’s there and how to stop it from coming back.
Read through our step-by-step guide and take the driver’s seat in combating car mold to ensure your ride is not just clean, but healthily pristine.
1. Identify the Problem
Mold in cars often goes unnoticed until it becomes a significant issue. Identifying the problem early can save you time and money.
Common signs of mold include:
- Discoloration on surfaces
- A persistent musty smell
- Visible spots on seats, carpets, or other interior areas
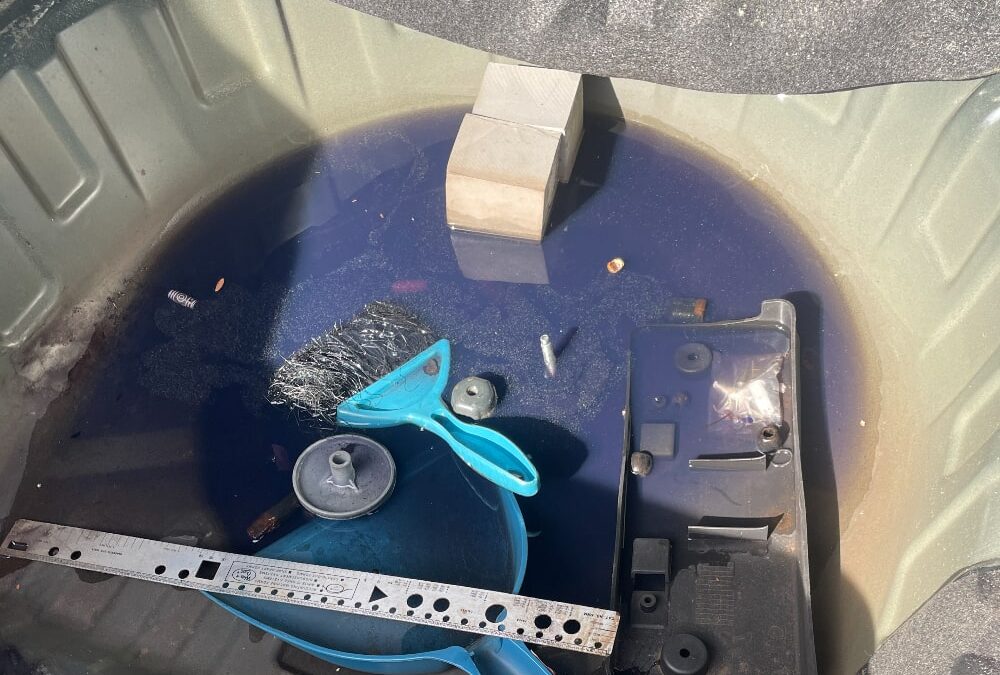
Mold can appear in various colors, such as black, green, white, or orange, and might have a fuzzy or slimy texture.
The presence of mold in your vehicle isn’t just a minor inconvenience. It poses health risks, particularly for those with allergies, asthma, or weakened immune systems. Mold spores can cause respiratory problems, skin irritation, and other health issues.
Addressing mold quickly and effectively is crucial to ensure the safety and well-being of everyone who uses the car.
2. Gather Necessary Supplies
Before starting the mold removal process, gather all the necessary supplies. You’ll need protective gear like gloves, masks, and goggles to protect yourself from mold spores.
Essential cleaning supplies include:
- White vinegar
- Baking soda
- A spray bottle
- Microfiber cloths
- A brush with stiff bristles
- A vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter
Protective gear is essential during vehicle mold removal to prevent inhalation of spores or skin contact. Mold spores can become airborne during the cleaning process which can pose a risk to your health. Wearing gloves, a mask, and goggles will help you avoid exposure and stay safe while tackling the mold problem.
3. Ventilate the Car
Proper ventilation is crucial when dealing with mold. Begin by opening all the car doors and windows to allow fresh air to circulate. If possible, park your car in a well-ventilated area, preferably outdoors.
This step helps to disperse mold spores and reduces the concentration of airborne particles.
Ventilating your car effectively involves creating a continuous flow of fresh air. You might consider using fans to enhance air circulation inside the vehicle.
This step not only helps in reducing mold spores but also aids in drying out the car and makes the subsequent cleaning steps more effective.
4. Remove Loose Items
Start by removing all loose items from your car, including floor mats, seat covers, and personal belongings. Mold can spread to these items, so it’s essential to clean or dispose of them properly.
Inspect each item for signs of mold. If you find mold on personal items, decide whether to clean them thoroughly or discard them to prevent re-contamination.
Clearing out the car interior also gives you a better view of the affected areas and allows you to assess the extent of the mold problem. By removing loose items, you ensure that you can clean every corner of your car more effectively.
5. Vacuum the Interior
Thoroughly vacuuming your car’s interior is a crucial step in removing mold spores. Use a vacuum cleaner equipped with a HEPA filter to ensure that you capture as many spores as possible. Focus on the seats, carpets, and any hard-to-reach areas where mold might be hiding.
Pay extra attention to the carpets and seats, as these are common places for mold growth. Use different attachments to get into crevices and under the seats.
Vacuuming not only removes visible mold but also helps in reducing the overall spore count which makes the subsequent cleaning steps more effective.
6. Clean with White Vinegar Solution
White vinegar is an effective, natural mold cleaner. Mix a solution of equal parts white vinegar and water in a spray bottle. Spray the solution generously on all mold-affected areas, including seats, carpets, and other interior surfaces. Allow the solution to sit for at least 15 minutes to penetrate the mold.
After the solution has had time to work, use a stiff-bristled brush to scrub the surfaces thoroughly. This helps to dislodge mold from deep within fabrics and crevices.
Wipe the surfaces with a microfiber cloth to remove the loosened mold and vinegar solution. Repeat this process as needed until all visible mold is gone.
7. Apply Baking Soda
Note: Make sure carpet is completely dry before performing this step. Baking soda is a great natural deodorizer and moisture absorber. Sprinkle a generous amount of baking soda over the affected areas, especially on carpets and upholstery.
Allow the baking soda to sit for several hours or overnight. This step helps to absorb any remaining moisture and neutralize odors caused by the mold.
After the baking soda has had time to work, vacuum it up using your HEPA-filter vacuum cleaner. This step not only removes the baking soda but also any remaining mold spores to leave your car smelling fresh and clean.
8. Use an Antifungal Spray
For a more thorough clean, use an antifungal spray designed specifically for mold removal. Choose a product that is safe for use on car interiors and follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Spray the antifungal solution on all affected areas, ensuring even coverage. The antifungal spray works to kill any remaining mold spores and prevent new mold growth.
Allow the solution to sit for the recommended time before wiping it off with a clean cloth. Using an antifungal spray adds an extra layer of protection and ensures that your car remains mold-free.
9. Dry the Car Thoroughly
Drying your car thoroughly is crucial to prevent mold from returning. Mold thrives in moist environments, so removing all moisture is essential.
Use fans or dehumidifiers to speed up the drying process. Open all doors and windows to enhance air circulation.
Focus on drying out the carpets, seats, and any other areas that may have been wet during the cleaning process. Use towels to blot any remaining moisture, and consider using a moisture meter to ensure that all areas are completely dry.
Thorough drying prevents future mold growth and keeps your car’s interior safe.
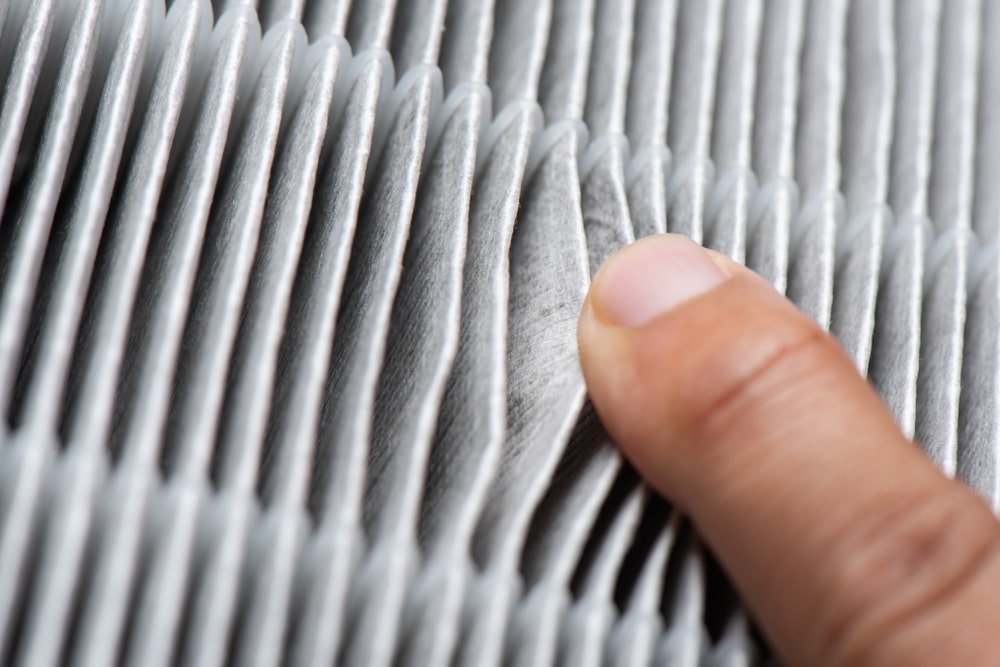
10. Inspect and Clean the Air Conditioning System
Keeping your car’s air conditioning system in top shape is essential for maintaining a mold-free environment. Start by inspecting and replacing the cabin air filter, a common hideout for mold spores. A fresh filter ensures cleaner air and less risk of mold recirculation.
Next, tackle the vents. Use a brush and an antifungal spray designed for use in automotive interiors to thoroughly clean each vent. This will remove any mold present and prevent spores from spreading.
For ongoing car interior care, regularly run your air conditioning on both cool and warm settings. This practice helps to dry out any residual moisture in the system and cuts down on the conditions that mold needs to grow.
It’s also wise to have a professional check your AC system annually. They can clean deeper components like the evaporator coil, which can be a breeding ground for mold if not properly maintained.
Implementing these car cleaning tips will not only improve your vehicle’s air quality but also enhance its overall cleanliness.
11. Prevent Future Mold Growth
Preventing mold in your vehicle is about maintaining a clean and dry environment. Regularly clean your car’s interior surfaces using car mold cleaning solutions that are specifically formulated to prevent mold growth.
Pay special attention to areas prone to moisture, such as floor mats and seats, which should be thoroughly dried if they become wet.
To further prevent car mold, ensure your vehicle is well-sealed. Check window seals and door gaskets regularly for any damage and replace them if they’re worn out. This keeps moisture from seeping into the car, a crucial step in mold prevention.
Another effective strategy is using moisture absorbers or dehumidifiers, especially if you live in a humid area. These tools can significantly reduce the dampness inside your car and create a less hospitable environment for mold.
Also, whenever possible, park your car in well-ventilated, sunny spots to help keep the interior dry and prevent mold.
Say Goodbye to Mold in Cars
Mold in cars is more than a mere inconvenience. It’s a silent aggressor against both your vehicle’s integrity and your health. Throughout this article, we’ve outlined a clear, step-by-step process to not only remove mold but ensure it doesn’t come back.
At Lonadier’s Mobile Detailing, we specialize in transforming your car into a pristine, safe haven free from mold and its spores. Our expertise in car mold remediation, backed by over a decade of dedicated service and stellar customer reviews, makes us your best ally in combating vehicle mold.
Don’t let mold take the driver’s seat. Contact us today and breathe new life into your ride.