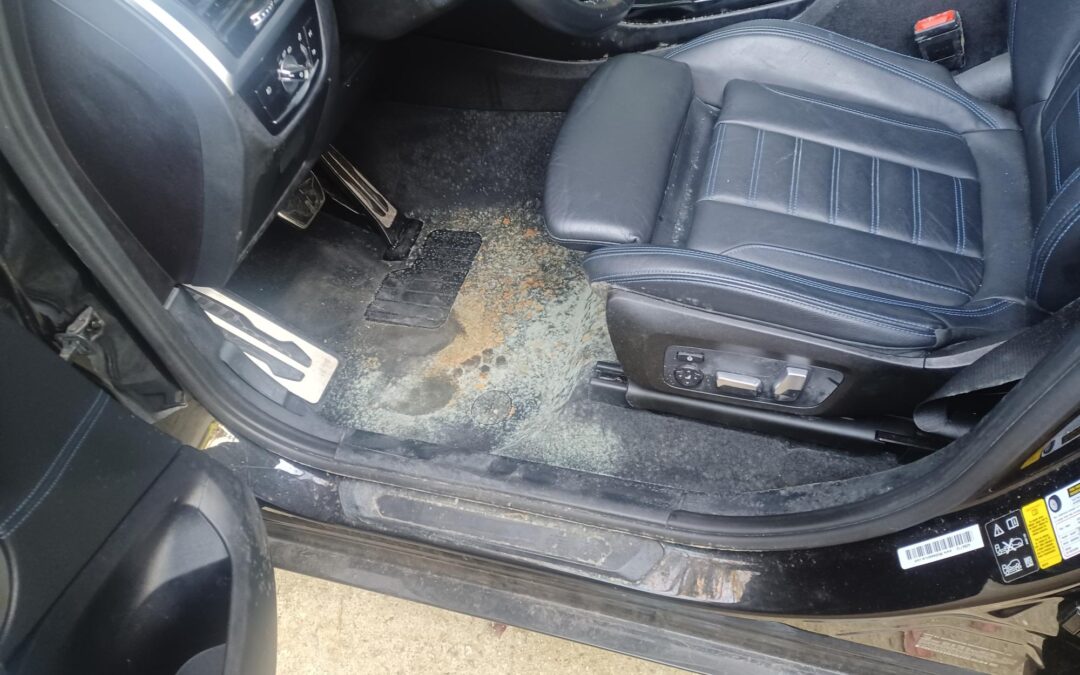
White mold is a common issue in homes and buildings, and cars typically forming in areas with excess moisture. Unlike darker molds, white mold can sometimes be mistaken for efflorescence or other substances, but it’s equally important to address due to potential health risks. Let’s explore the most common types of white mold, how to identify them, and tips for prevention.
-
Penicillium
Penicillium is a fast-growing mold that thrives on organic material like food, wood, and insulation. It can appear in various shades, including white, especially in the early stages. This mold type is known for its powdery or velvety texture and is often found in humid, damp areas such as basements and bathrooms. Certain strains produce toxins that can irritate the respiratory system.
-
Cladosporium
Cladosporium molds are usually found on walls, carpets, and fabrics in humid environments. Although this mold is often dark green or black, it can appear as white in its early stages or when it grows in specific conditions. Cladosporium can cause allergic reactions, asthma, and sinus infections in sensitive individuals.
-
Aspergillus
Aspergillus is a highly adaptable mold that can appear white, especially when it’s just starting to develop. This type of mold grows on a wide range of surfaces, including drywall, fabrics, and even in air-conditioning systems. Aspergillus can produce mycotoxins, which are harmful to humans if inhaled, ingested, or contacted.
-
Trichoderma
This mold often appears white and fuzzy, turning to darker shades as it matures. Trichoderma is commonly found on wallpaper, carpets, and wood surfaces. Known to produce enzymes that can break down organic matter, this mold can be particularly damaging to the structures in a home. It also releases mycotoxins that may pose health risks, especially for people with weakened immune systems.
-
Acremonium
Acremonium starts as a moist, white mold that later becomes powdery. Often found in areas with high humidity or water damage, such as condensation lines, window sills, and drain pans, Acremonium has a slow growth rate but can spread over time if not controlled. Like other molds, it can lead to respiratory symptoms if left unchecked.
How to Identify White Mold
White mold can look like powder or a thin, fuzzy layer on surfaces. It often appears as white, off-white, or slightly gray, making it tricky to identify without closer inspection. To test for mold, consider consulting a professional or using a mold testing kit, as distinguishing it from non-harmful substances like efflorescence can be challenging.
Preventing and Managing White Mold
- Control Humidity: Use dehumidifiers in areas prone to dampness, like basements or attics.
- Fix Leaks Promptly: Water intrusion from leaks can create ideal conditions for mold growth.
- Ventilate Properly: Ensure areas such as bathrooms and kitchens have good ventilation to prevent moisture buildup.
- Clean Regularly: Regularly clean surfaces prone to mold growth, like walls, ceilings, and around windows.
Final Thoughts
White mold might appear harmless, but it can pose health and structural risks over time. If you suspect white mold in your home, take action to identify and remove it, ideally with professional assistance.