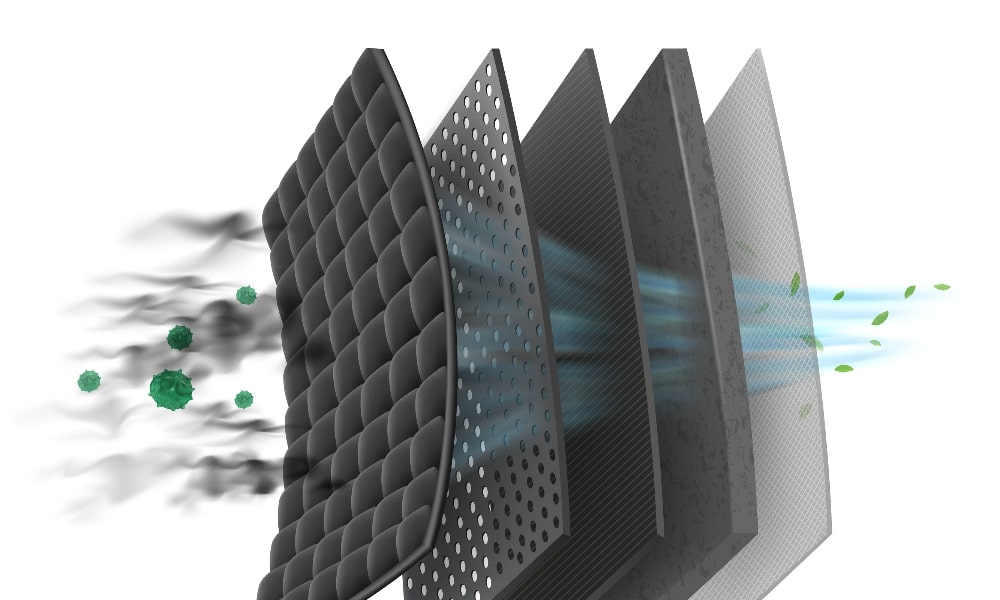
Imagine you’re driving down a scenic route with your family, the sun shining and a cool breeze flowing through the open windows. Suddenly, you hit a cloud of dust from a nearby construction site. Instinctively, you close the windows, but the air inside the car still feels stuffy and unpleasant.
Have you ever wondered how much of that dust and pollution is being filtered out before it reaches your lungs? The answer lies in your car’s air filter. Just as we rely on clean air to breathe easily at home or work, the air quality inside your vehicle is crucial for your health and comfort.
But what are some of the other benefits?
Let’s go through the importance of a good air filter in a car.
Protect Respiratory Health
One of the top car air filter benefits that you shouldn’t neglect is how it can help your health.
As you drive, the air inside your car’s cabin can be infiltrated by a variety of airborne pollutants. That includes dust, pollen, mold spores, and other microscopic particles.
These contaminants can exacerbate allergies, asthma, and other respiratory conditions. That makes driving an uncomfortable and potentially harmful experience for many people.
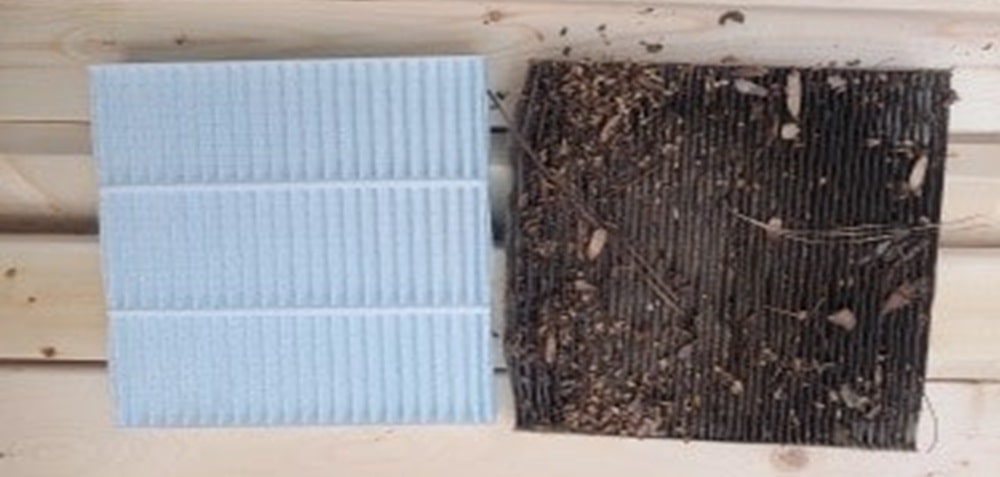
A high-quality air filter is designed to trap these particles before they enter the cabin, significantly reducing your exposure to allergens and pollutants. By maintaining a clean air filter, you create a healthier environment within your vehicle, which is especially crucial for individuals with pre-existing respiratory issues.
Good air quality can majorly lower the risk of developing respiratory problems over time, providing long-term health benefits for you and your passengers.
Cut Down on Allergens
Common allergens like plant pollen, dust mites, and pet dander can quickly make their way into your car, especially during certain seasons or if you frequently drive with the windows down.
These allergens can cause annoying allergic reactions, with symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and coughing, which can be particularly problematic for those with seasonal allergies or chronic respiratory conditions.
For drivers who suffer from allergies, the benefits are immediate and noticeable. Driving becomes less of a chore and more of a pleasant experience when you’re not constantly dealing with allergy symptoms.
This improved air quality can make a significant difference on longer trips, reducing the cumulative exposure to allergens and enhancing overall comfort.
An efficient air filter also helps to minimize the spread of allergens between passengers. If you frequently transport pets or have passengers with different allergy sensitivities, a good air filter ensures that everyone can enjoy a cleaner, healthier ride.
Ongoing maintenance and quick replacement of your car’s air filter are key to keeping allergens at bay and ensuring the best air quality possible for all occupants.
Get Rid of Bad Smells
Car odors can also be a concern. Driving with lingering smells from outside pollutants, such as exhaust fumes, industrial emissions, or even natural scents like skunk spray, can make any journey uncomfortable.
These odors can seep into the cabin and persist. That creates an unpleasant environment for you and your passengers.
Activated carbon air filters are particularly effective in neutralizing these bad smells. Unlike regular filters that only trap particles, activated carbon filters absorb and eliminate odors. That way, the cabin air will be fresh and clean.
This type of filter contains carbon treated with oxygen. This creates a highly porous material capable of capturing gaseous pollutants and smells.
Common sources of interior odors include food spills, pet smells, and even cigarette smoke.
Over time, these odors can become embedded in the upholstery and ventilation system, making them difficult to eradicate. An efficient air filter helps to mitigate these smells by continually filtering the air and trapping odor-causing particles.
Improved HVAC Efficiency
When your car’s air filter gets stuffed up clogged with debris, it restricts airflow, forcing the HVAC system to have to work harder to spread air throughout the vehicle.
This increased strain can increase your general higher energy consumption and reduced system performance.
A good air filter ensures that the HVAC system operates efficiently by allowing unobstructed airflow. This improves the system’s ability to maintain a comfortable temperature inside the cabin. It also enhances its capacity to filter and purify the air.
With a clean air filter, the HVAC system can effectively remove airborne particles, providing cleaner, healthier air for you and your passengers.
Better Fuel Efficiency
A good air filter ensures that the HVAC system operates efficiently by allowing unobstructed airflow. This not only improves the system’s ability to keep up a comfortable temperature inside the cabin but also enhances its capacity to filter and purify the air.
With a clean air filter, the HVAC system can effectively remove airborne particles, providing cleaner, healthier air for you and your passengers.
Keep Your Engine Safe
Did you know that better car air quality can help your engine work better?
The engine air filter plays a vital role in preventing harmful contaminants from entering the engine. Dust, dirt, sand, and other debris can cause significant damage if they penetrate the engine’s internal components. Over time, these particles can lead to increased wear and tear, reducing the engine’s efficiency and potentially leading to costly repairs.
A high-quality air filter acts as the first line of defense against these contaminants. It traps particles before they can enter the engine, ensuring that only clean air reaches the combustion chamber.
When the engine receives a sufficient supply of clean air, it can mix the air-fuel ratio properly, ensuring efficient combustion. This leads to smoother acceleration, improved power output, and overall better engine responsiveness.
A dirty air filter restricts airflow, causing the engine to work harder and potentially overheat, which can lead to performance issues and mechanical failures.
More Comfortable
If you want to stay more comfortable while you drive, look into changing out your air filter.
Whether you need to cool down during a hot summer day or warm up on a chilly morning, a well-functioning air filter ensures that your HVAC system delivers the desired temperature quickly and effectively.
A clean air filter reduces the likelihood of fogging up windows. Particles and contaminants can contribute to humidity levels inside the car, causing windows to fog up more easily.
It helps maintain proper airflow and reduces humidity. That ensures clear visibility and a safer, more comfortable driving experience.
The overall ambiance of the vehicle is improved with a clean air filter. Passengers appreciate a fresh and pleasant-smelling cabin, and the reduced presence of dust and allergens makes for a more enjoyable ride.
Whether you are on a short commute or a long road trip, the comfort provided by a clean air filter can make a significant difference.
Choosing the Best Car Air Filters
With various types of air filters available on the market, it’s essential to understand their differences and choose one that best meets your needs.
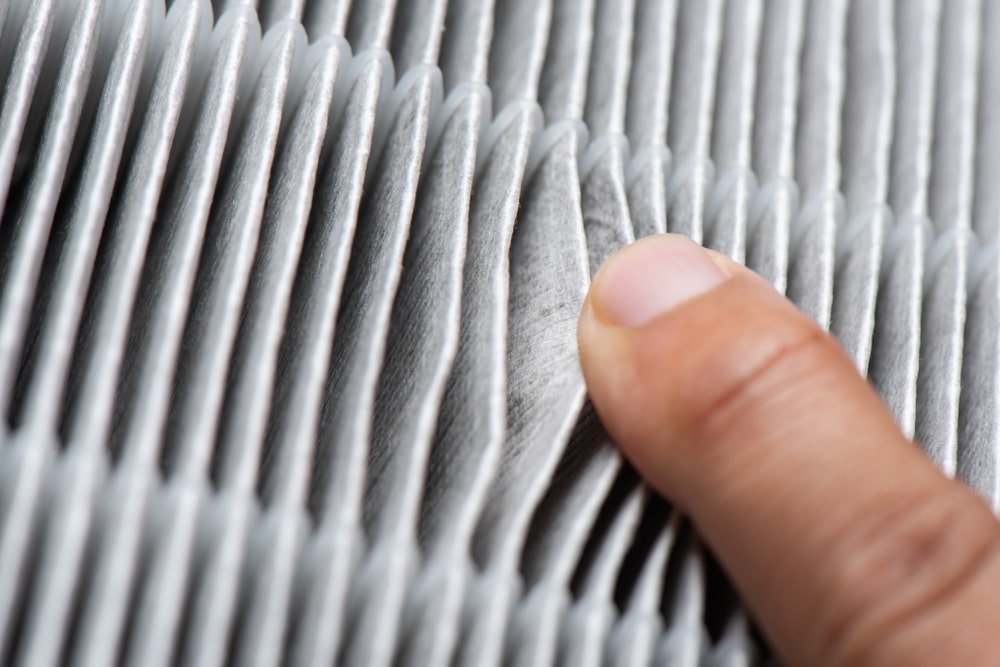
Paper filters are the most common and cost-effective filters, typically made from pleated paper. They effectively trap large particles and are disposable. However, they may need more frequent replacements than other types.
Foam filters can be cleaned and reused. They offer good filtration for larger particles but may not be as effective at capturing finer particles.
Often used in high-performance vehicles, cotton filters are washable and reusable. They provide excellent filtration and airflow, making them a popular choice for those looking for long-term performance.
HEPA filters are meant to trap super tiny particles, including allergens and pollutants. They offer superior filtration but can be more expensive than other types.
Some filters contain activated carbon to remove odors and gases in addition to particles. They are ideal for drivers who often encounter strong smells, such as exhaust fumes or industrial pollutants.
Car Air Filter Maintenance
Proper maintenance of your car’s air filter is essential for ensuring optimal air quality, engine performance, and overall comfort. Regularly inspecting and replacing your vehicle’s air filter is a simple yet crucial task that can significantly impact your vehicle’s functionality and longevity.
Pay attention to signs that your air filter may need replacement sooner than scheduled. Reduced airflow from the HVAC system, unusual engine noises, decreased fuel efficiency, or persistent odors in the cabin can all indicate a clogged or damaged air filter.
Maintaining a record of your air filter inspections and replacements can help you stay on track with regular maintenance. Note the date and mileage of each inspection or replacement, and set reminders for future checks.
This practice ensures that you never overlook this essential maintenance task, keeping your car in optimal condition.
Addressing these issues promptly can prevent further damage and maintain your vehicle’s performance. Don’t be afraid to bring in some professional help with your air quality maintenance, too!
Enjoy the Benefits of a Good Air Filter in a Car
There are so many reasons you’ll want a good air filter in a car. If you haven’t considered them before, it might be time to get on top of this issue.
Do you want help with your automobile health maintenance? Lonadier’s Mobile Detailing has over a decade of experience with mold remediation, just one more way you can improve automobile air quality.
Contact us