What You Need to Know About the Air Quality Index in Your Car!
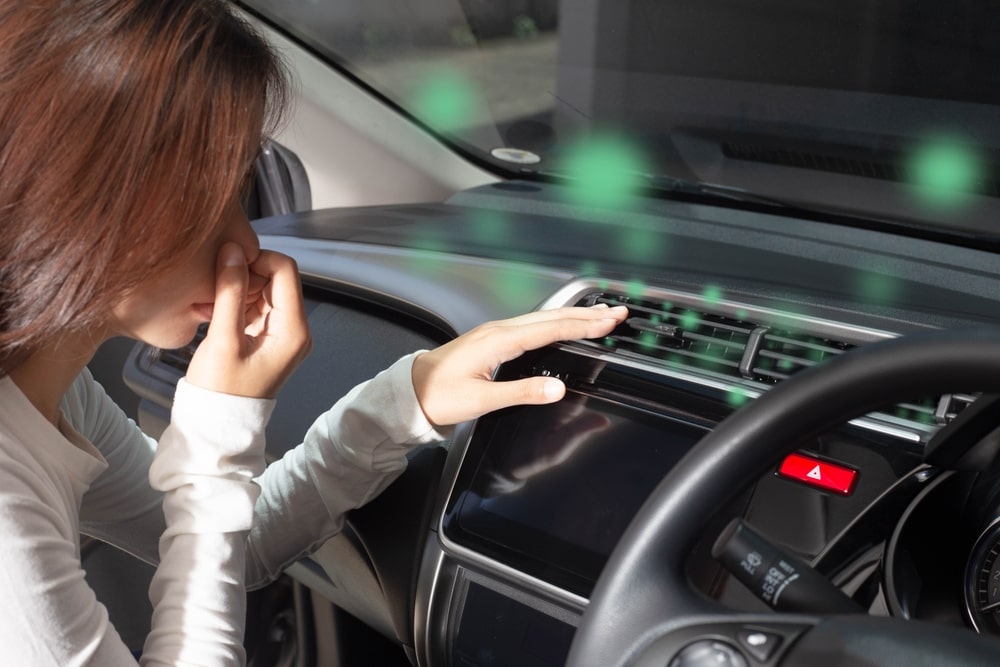
Maintaining good air quality in your car is essential for the health and comfort of occupants. The air quality index (AQI) in cars can be influenced by various factors, including pollutants, allergens, and mold. Here’s what you need to know about monitoring and improving air quality in your car:
Factors Affecting Air Quality in Cars
- External Pollutants:
- Traffic Emissions: Exhaust fumes from other vehicles can enter your car, especially in heavy traffic.
- Industrial Pollution: Driving near factories or industrial areas can expose you to higher levels of pollutants.
- Pollen and Allergens: Seasonal changes can increase the presence of pollen and other allergens inside the car.
2. Internal Pollutants:
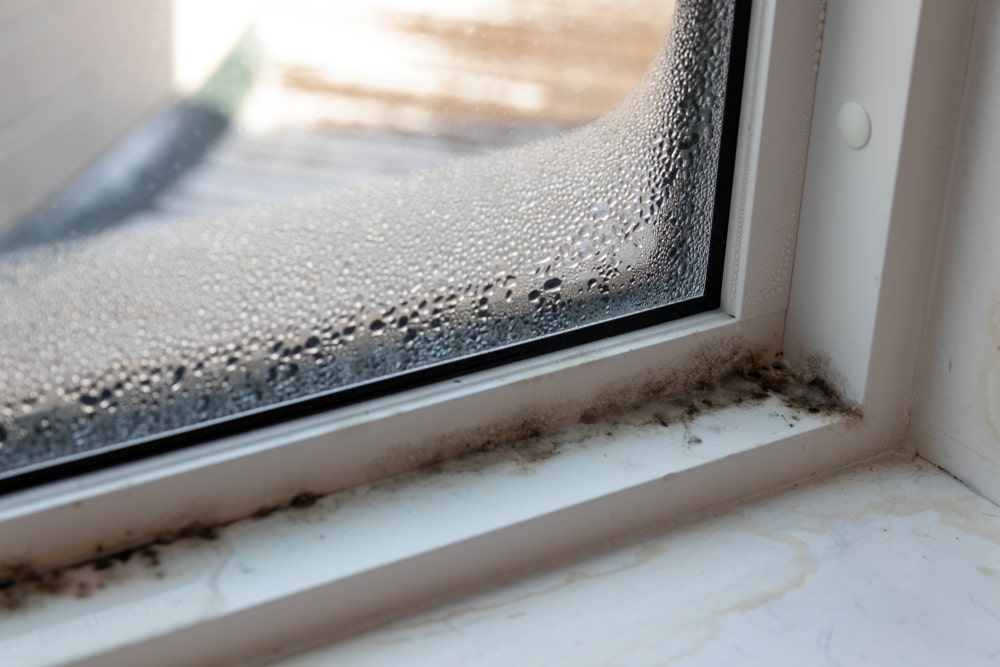
- Mold and Mildew: Moisture buildup from leaks or condensation can lead to mold growth inside the car.
- Dust and Particles: Accumulation of dust, pet dander, and other particles can degrade air quality.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): These can be emitted from car interior materials like upholstery, plastics, and cleaning products.
Monitoring Air Quality in Cars
To monitor the air quality inside your car, consider using the following tools:
- Portable Air Quality Monitors:
- Devices that measure levels of pollutants like particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), carbon dioxide (CO2), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and more.
- These monitors can provide real-time data on air quality and alert you to hazardous levels of pollutants.
- Built-in Air Quality Sensors:
- Some modern vehicles come equipped with built-in air quality sensors that monitor and display air quality levels.
- These systems often work in conjunction with advanced air filtration systems to maintain good air quality automatically.
How AQI is Determined
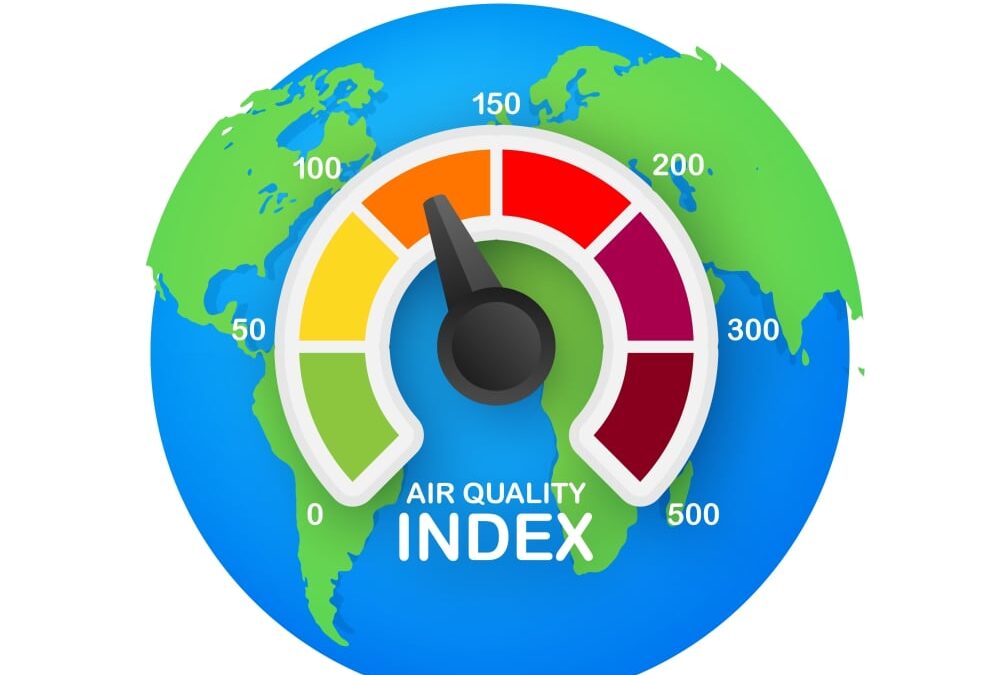
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a numerical scale used to communicate how polluted the air currently is or how polluted it is forecast to become. The AQI incorporates multiple air pollutants and provides a single value to represent overall air quality. The specific pollutants considered in the AQI can vary by country, but commonly included pollutants are:
- Ground-level ozone (O3)
- Particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
The AQI is calculated based on the concentration levels of these pollutants. Each pollutant is assigned an individual index value, and the highest of these values is used as the overall AQI for a specific location and time. The AQI is typically reported on a scale from 0 to 500, where higher values indicate poorer air quality.
The general steps for calculating the AQI are as follows:
- Measure pollutant concentrations:The concentrations of each relevant pollutant are measured at various monitoring stations.
- Determine sub-index values:Each pollutant’s concentration is converted into a sub-index value using a specific formula. These formulas are often nonlinear and are designed to reflect the known health effects of each pollutant.
- Choose the highest sub-index:The highest sub-index value among all pollutants is selected as the overall AQI for that location and time.
- Interpret the AQI:The AQI is divided into categories or color-coded ranges that correspond to different levels of health concern. These categories typically range from “Good” to “Hazardous,” providing a quick indication of the potential health risks associated with the current air quality.
Air Quality Index ratings:
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a numerical scale used to communicate the quality of the air to the public. It is measured by assessing the levels of specific air pollutants in the atmosphere, such as ground-level ozone, particulate matter, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen dioxide. The AQI scale typically ranges from 0 to 500, with higher values indicating worse air quality.
To measure the AQI, monitoring stations collect data on these pollutant levels, usually on an hourly basis. The concentration of each pollutant is then converted to an individual AQI value using a standardized formula, which takes into account the pollutant’s health effects at various concentrations. The highest individual AQI value among the pollutants measured at a given location becomes the overall AQI for that area.
Six Categories of Air Quality
The AQI is divided into six color-coded categories, each representing a different level of health concern:
Good (0-50): Air quality is considered satisfactory, and air pollution poses little or no risk.
Moderate (51-100): Air quality is acceptable; however, there may be a moderate health concern for a very small number of people who are unusually sensitive to air pollution.
Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups (101-150): Members of sensitive groups, such as children, older adults, and people with respiratory or heart issues, may experience health effects. The general public is not likely to be affected.
Unhealthy (151-200): Everyone may begin to experience health effects, and members of sensitive groups may experience more serious health effects.
Very Unhealthy (201-300): Health alert, meaning everyone may experience more serious health effects.
Hazardous (301-500): Health warnings of emergency conditions, as the entire population is more likely to be affected.
It’s important to note that different countries may use different AQI systems with variations in the pollutants considered, concentration ranges, and health categories. The AQI is a useful tool for informing the public about air quality and helping individuals take appropriate actions to reduce exposure when air quality is poor.
Improving Air Quality in Cars
Here are some steps to improve and maintain good air quality in your car:
Improving the air quality index (AQI) in your car involves a combination of measures to reduce the intake of external pollutants, control internal sources of contamination, and maintain a clean and well-ventilated environment. Here are some effective strategies to improve AQI in your car:
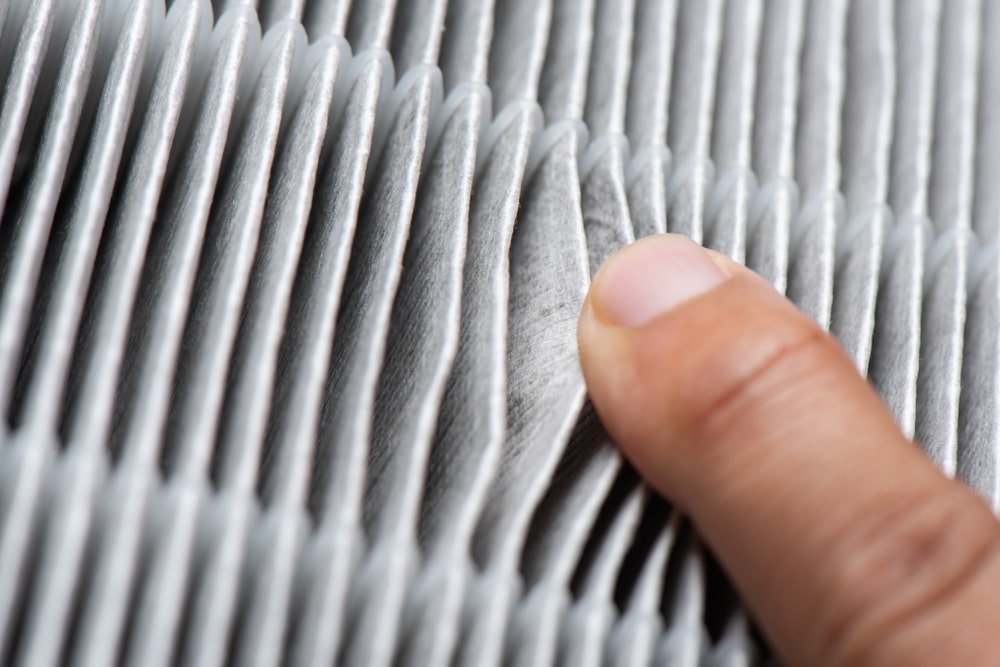
1. Use High-Quality Air Filters
- Cabin Air Filters: Install and regularly replace the cabin air filter with a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter. HEPA filters are capable of trapping fine particles, including dust, pollen, and other allergens.
- Regular Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for changing the filter, typically every 12,000 to 15,000 miles, or more frequently if you drive in high-pollution areas.
2. Improve Ventilation
- Use Recirculation Mode Wisely: Use the recirculation mode in heavy traffic or polluted areas to minimize the intake of outdoor pollutants. However, periodically switch to fresh air intake to avoid CO2 buildup and to bring in fresh air.
- Fresh Air Intake: When driving in areas with good air quality, use the fresh air intake to allow proper ventilation and reduce indoor pollutant levels.
3. Control Moisture and Prevent Mold
- Fix Leaks: Address any leaks in your car to prevent moisture buildup, which can lead to mold growth.
- Use Dehumidifiers: Consider using car dehumidifiers or moisture-absorbing products, especially in humid climates, to control humidity levels inside the car.
- Dry Wet Areas: Promptly dry any wet areas, such as carpets and seats, to prevent mold and mildew.
4. Keep the Interior Clean
- Regular Cleaning: Vacuum and clean the car interior regularly to remove dust, dirt, pet dander, and other allergens.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Use low-VOC or natural cleaning products to reduce the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
5. Use Air Purifiers
- Portable Air Purifiers: Use portable air purifiers designed for cars to filter out pollutants and improve air quality. Look for purifiers with HEPA filters and activated carbon filters.
- Ionizers: Some car air purifiers come with ionizers that can help reduce airborne particles.
6. Monitor Air Quality
- Air Quality Monitors: Use portable air quality monitors to measure levels of pollutants like particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), VOCs, and CO2. This can help you understand the air quality inside your car and take appropriate actions.
- Built-in Sensors: If your car has built-in air quality sensors, monitor the display and adjust ventilation settings as needed.
7. Avoid Pollutant Sources
- No Smoking: Avoid smoking inside the car, as it significantly degrades air quality and leaves harmful residues.
- Limit Idling: Reduce idling time, especially in enclosed spaces like garages, to minimize the buildup of exhaust fumes inside the car.
8. Maintain HVAC System
- Regular Service: Ensure that your car’s HVAC system is regularly serviced and cleaned to maintain optimal performance and air quality.
- Clean Ducts: Consider having the air ducts cleaned periodically to remove any dust, mold, or debris buildup.
9. Improve Driving Habits
- Windows Up: Keep windows up when driving in high-pollution areas or during pollen season to reduce the intake of external pollutants.
- Avoid High Traffic Areas: Whenever possible, avoid driving in heavy traffic or industrial areas where pollutant levels are higher.
By implementing these strategies, you can significantly improve the air quality inside your car, providing a healthier and more comfortable environment for you and your passengers. Regular maintenance, proper ventilation, and the use of high-quality filters and purifiers are key to achieving and maintaining good AQI in your vehicle.
Maintaining good air quality in your car involves monitoring for pollutants, using high-quality air filters, controlling moisture, and keeping the interior clean. By taking these steps, you can ensure a healthier and more comfortable environment for you and your passengers.
What to Avoid to Maintain a Healthy AQI
To maintain a healthy air quality index (AQI) in your car, it’s important to avoid certain practices and conditions that can deteriorate the air quality. Here are key things to avoid:
1. Smoking Inside the Car
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking in the car releases harmful chemicals, particulate matter, and carcinogens, which can significantly degrade air quality and leave residues that are hard to remove.
2. Using Harsh Chemical Cleaners
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Cleaning products with strong chemicals and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can release harmful fumes. Instead, use low-VOC or natural cleaning products.
3. Allowing Moisture Build-Up
- Avoid Moisture Accumulation: Moisture can lead to mold and mildew growth, which can release spores and degrade air quality. Ensure leaks are repaired, and wet items are promptly dried.
- Don’t Ignore Leaks: Address any leaks from windows, sunroofs, or the HVAC system immediately.
4. Ignoring Air Filter Maintenance
- Avoid Neglecting Filters: Failing to replace or clean the cabin air filter regularly can reduce its effectiveness in trapping dust, pollen, and other pollutants.
- Use Low-Quality Filters: Invest in high-quality HEPA filters rather than cheaper, less effective ones.
5. Poor Ventilation Practices
- Avoid Constant Recirculation Mode: While recirculation mode can be useful in high-traffic areas, using it constantly can lead to increased levels of CO2 and reduced oxygen levels inside the car.
- Don’t Overlook Fresh Air Intake: Occasionally use the fresh air intake mode to allow ventilation and reduce indoor pollutant levels.
6. Ignoring Regular Cleaning
- Avoid Neglecting Cleaning: Accumulation of dust, dirt, and pet dander can affect air quality. Regularly vacuum and clean the car’s interior, including hard-to-reach areas.
- Skip Detailed Cleaning: Pay attention to cleaning not just visible surfaces but also areas like under the seats and in the HVAC ducts.
7. Leaving Food and Trash Inside
- Avoid Leaving Food and Trash: Food crumbs and trash can attract pests and lead to the growth of bacteria and mold. Regularly remove all trash and avoid eating inside the car when possible.
8. Using Air Fresheners with Strong Chemicals
- Avoid Chemical Air Fresheners: Many air fresheners contain chemicals that can emit VOCs. Opt for natural air fresheners or essential oil diffusers instead.
9. Driving with Windows Open in Polluted Areas
- Avoid Open Windows in High Traffic: Keep windows closed in high-traffic or industrial areas to prevent outdoor pollutants from entering the car.
- Use A/C Wisely: Use the air conditioning system with the appropriate settings to maintain good air quality without pulling in excessive pollutants.
10. Ignoring HVAC System Maintenance
- Avoid Skipping HVAC Maintenance: Regularly service the car’s HVAC system to ensure it’s clean and functioning efficiently. This includes cleaning or replacing air ducts and ensuring there’s no mold or debris buildup.
By avoiding these practices and maintaining proper car care and hygiene, you can significantly improve and maintain a healthy AQI inside your vehicle. Regular maintenance, conscious use of ventilation settings, and attention to cleaning and filter replacement are key factors in ensuring good air quality for a safe and comfortable driving environment.